|
|
|
Embolism
Embolism = obstruction of a downstream
blood vessel by a solid, liquid or gaseous mass (embolus)
which has entered the circulation upstream.
Emboli may include:
-
air bubbles
-
nitrogen or helium bubbles
-
fat globules
-
tissues, e.g. intervertebral disc material
-
neoplastic cells
-
parasites, bacteria or fungi
-
fragments of thrombi (thromboemboli)
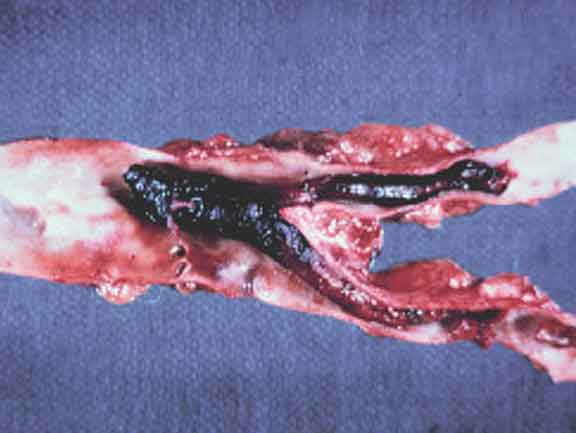
A saddle thromboembolus in the terminal aorta of a cat with cardiomyopathy.
The thromboembolus is a detached fragment from an upstream thrombus, most
likely located in the left atrium.
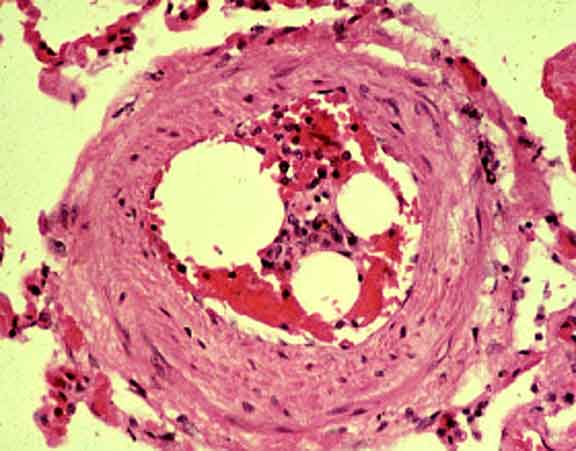
Lipid emboli within a pulmonary artery in a human. Lipid emboli are
always microscopic in size.
|


