Introduction
Haemorrhage
The escape of blood from the cardiovascular system is termed haemorrhage. Haemorrhage is usually referred to as internal or external.
Internal haemorrhage is into tissues or body cavities.
External haemorrhage is lost from the body; sources include peripheral tissues (e.g. skin, subcutis) or alimentary, respiratory or urogenital tracts.
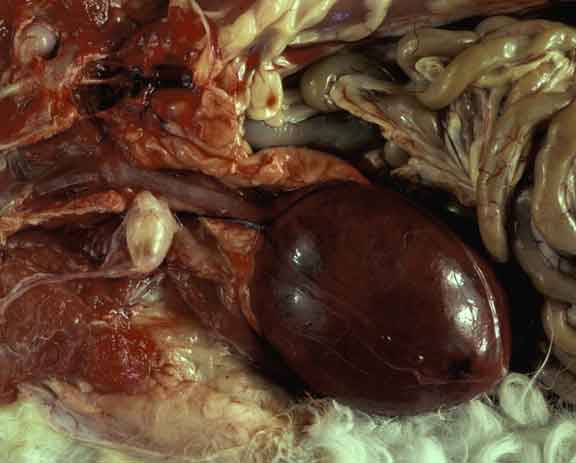
This dog died from acute haemoperitoneum as a result of slippage of a ligature placed during ovariohysterectomy.
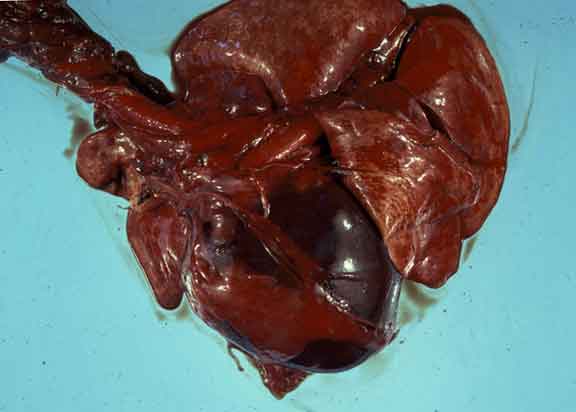
This dog died from acute haemopericardium due to haemorrhage into the pericardial sac from a tumour on the external aspect of the right auricle of the heart.
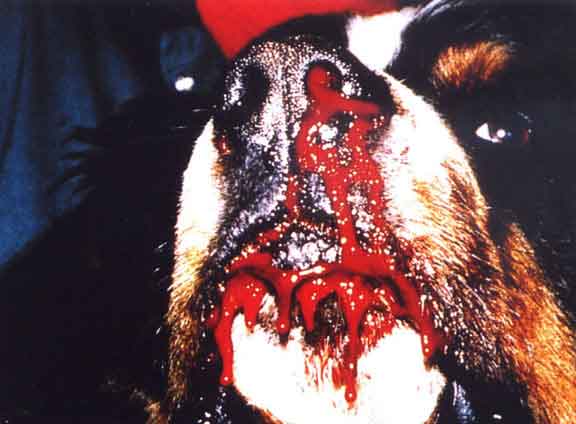
Haemorrhage from the nose is termed epistaxis.