|
|
|
Case 3:
History:
A 3 year old, prize-winning, male Himalayan cat had a protracted
recovery from general anaesthesia for tooth scaling. Over the 30 hour
period following anaesthesia, the cat was moribund and developed severe
azotaemia, hyperkalaemia, metabolic acidosis and anuria despite intravenous
fluid therapy. The cat was euthanised. At necropsy, there was marked subcutaneous
and mediastinal oedema, with hydropericardium, hydrothorax, ascites and
pulmonary oedema.
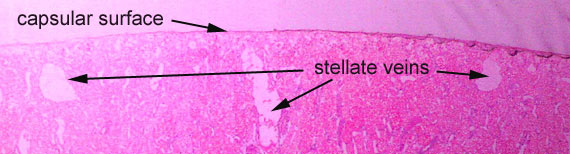
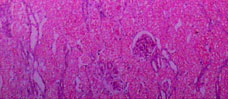
This is a low power view
of the outer renal cortex. As is typical of feline kidneys, there
are prominent subcapsular stellate venous channels.
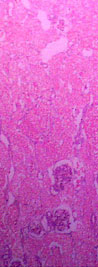
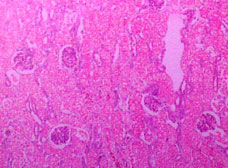
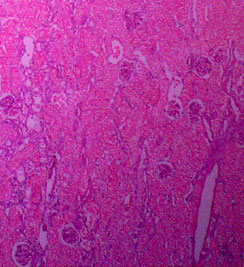
At this magnification, the cortex appears brightly eosinophilic
and there is increased prominence of glomeruli and of some tubules
because they stain basophilically.

|