|
|
|
Acute
Inflammation:
Acute inflammation is the immediate and early response
to tissue injury. It involves alterations to blood flow, increased vascular
permeability and leucocyte emigration. These result in heat, redness and
swelling of the region. Pain is the result of the release of substances
such as prostaglandins.
Vascular changes involve the following processes:
-
Brief vasoconstriction - only for a few seconds
-
Vasodilation - increased blood transport to the
area and elevated temperature
-
Increased permeability - allows protein rich fluid
(exudate) to enter tissues.This helps to dilute toxins and bacteria,
and increases the delivery of complement proteins to the region.
-
Stasis of blood flow - this maintains fluid accumulation
in the region and permits margination and emigration of neutrophils
through the vessel walls.
Neutrophils are the acute phase leucocytes and dominate
the first 2 days of most inflammatory reactions prior to the accumulation
of large numbers of macrophages.
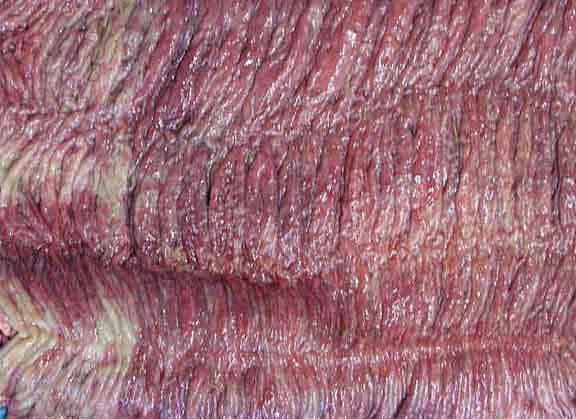

Inflamed colonic mucosa – foal. Redness is a hallmark
of inflammation.
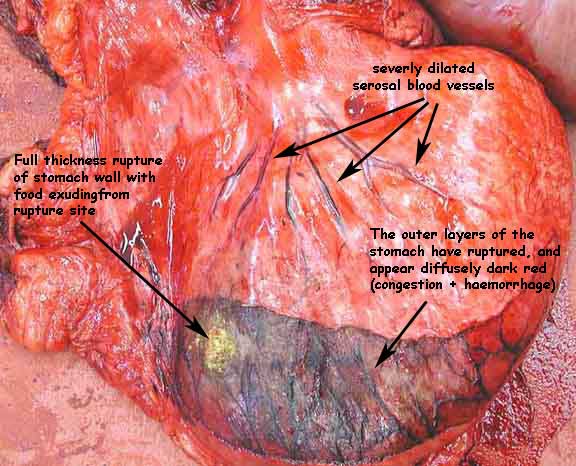
It is important to distinguish pre-mortem rupture of
gut from post-mortem rupture. In this case, there is pre-mortem rupture
of the stomach in this horse.
 
|


