| |
|
|
Classification
of Abnormalities:
1. Excessive division:
Polydactylia - extra toes
Polythelia - extra nipples
Polydontia - extra teeth
Polymastia - extra mammary glands
2. Failure to fuse normally:
Palatoschisis - cleft palate
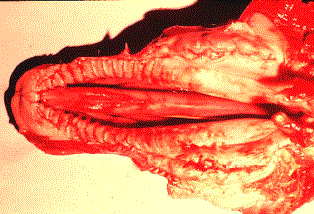
Calf - cleft palate (palatoschisis)

Horse - food material at the nostril of a horse with
cleft palate
Heiloshcisis - hair lip
Cranioschisis -skull is open
Spina bifida - fissure inspinal column
3. Arrested division:
Cyclopia - defect in development of frontal process
Rens arcuatas - horseshoe kidney
Syndactyly - fusion of bone of hands or feet
Failure to complete division of organs in twinning

Lamb - fused brains from a two headed lamb
4. Complete local failure of growth:
Amelia - absence of limbs
Acrassia - absence of cranial bones
Agnathia - absence of upper or lower jaw
Epitheliogenesis imperfecta - epithelium is absent, lesions
may be focal or generalised.

Dog - focal epitheliogenesis imperfecta
5. Arrest of development of final
form or position:
Ectopia cordis - heart outside pericardium or the thorax
Dextroposition of aorta
6. Persistence or disappearance of
contiguous structures:
Usually follow a pattern.
-
aortic arches
-
foramen ovale
-
patent urachus
-
ductus arteriosis
-
persisting Mullerian ducts

Dog - persistent right 4th aortic arch (arrow)
7. Over development of local tissues:
Polycystic kidneys - due to a biochemical defect in tubular
electrolyte pump which leads to buildup of fluid
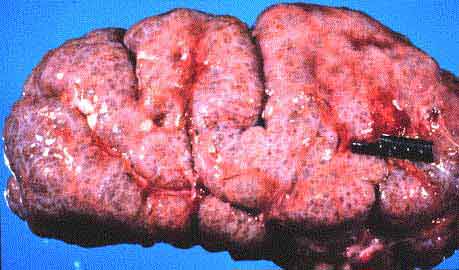
Polycystic kidney
Hamartomas - inappropriate mixtures of tissue
Teratoma
8. Displacement of tissue:
Keratoma
Dermoid cyst
9. Fusion of sexual characteristics:
True hermaphrodite
Pseudohermaphrodite
Free martin - these are more common in pigs, goats and
cattle
10. Persistence or disappearance
of contiguous structures:
Porphyria - coloured bones, urine
Ichthyosis - hair follicles do not erupt
Ostoegenesis imperfecta - fragile bones perhaps due to
osteoblastic defect
|
|






