| |
|
|
Haematogenous
Spread:
This pathway tends to be favoured by sarcomas but can
also occur with carcinomas (eg. thyroid, adrenocortical, renal and hepatocellular
carcinomas). Invasion is usually initially into capillaries or venules
rather than arterial channels.
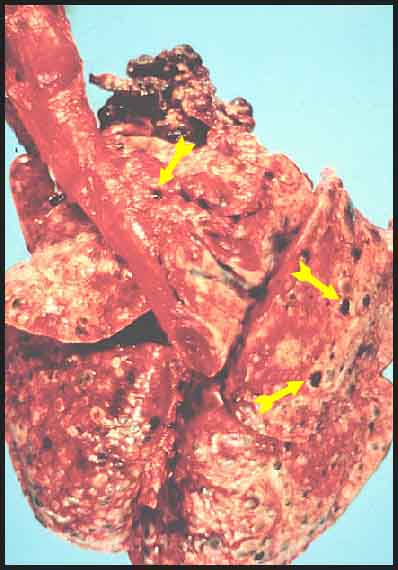
Haemangiosarcomas typically spread directly via blood
vessels rather than lymphatics. In this dog, a primary cardiac haemangiosarcoma
has metastasised to the lungs. (dark red nodules – yellow arrows)
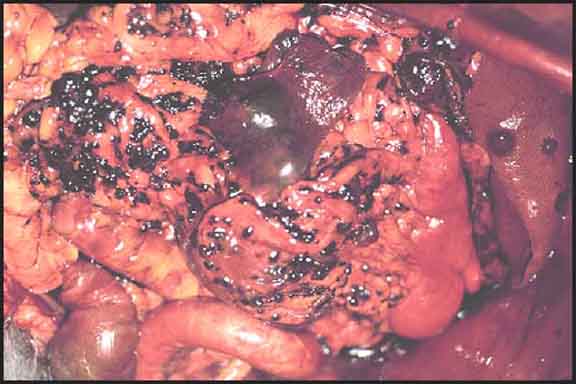
Haemangiosarcomas can also spread by implantation as
in this dog in which numerous peritoneal secondary tumours have resulted
from rupture of a primary splenic mass (small black shiny nodules).
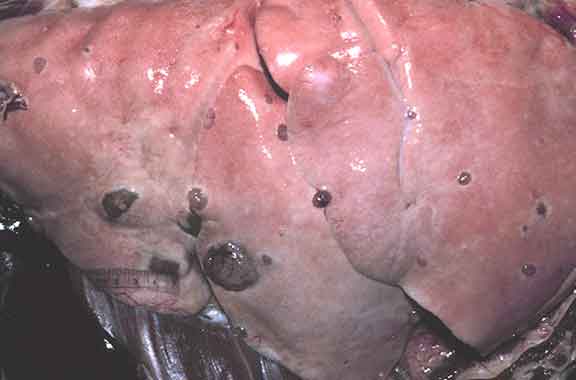
Metastatic myxosarcoma nodules in the lungs of a dog.
Malignant cells had spread directly via blood vessels from a subcutaneous
primary mass to the lungs, bypassing regional lymph nodes.

Some carcinomas commonly invade venous rather than lymphatic
channels. In this dog, an adrenocortical carcinoma has invaded the adrenal
vein and is advancing along the caudal vena cava (green arrow).

Carcinoma which has metastasized into lung via arteries
(arrowheads) (x100).
Haematogenous spread cases:
|
|





